Robots Can Now Reproduce
[Please note that this page contains affiliate links. If you choose to purchase after clicking a link, I may receive a commission at no extra cost to you.]
The United States inventors who produced the first alive robots say the life forms, called xenobots, can now reproduce, and it is different than how animals or plants reproduce.
The African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) is where its name derives from.
Reproducing Robots
Xenobots are not even a millimetre (0.04 inches) wide. The teeny dots were first presented in 2020 after research showed that they could move, self-heal, and work together in groups.
Researchers who developed them through the Harvard University’s Wyss Institute for Biologically, Inspired Engineering University of Vermont, and Tufts University alleged that they had found a new method of biological reproduction that is not like any plant or animal species that is known.
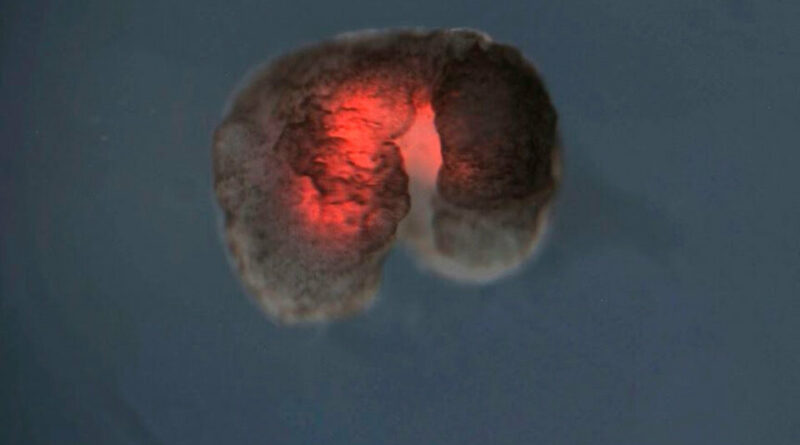
The parent xenobots are C-shaped.
They compress and collect loose stem cells into piles which then will mature into offspring.
Organism or Robot?
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that can mature into other cell types. The researchers made a xenobot by scraping the living stem cells from the embryos of frogs and letting them incubate. There is no gene manipulation involved whatsoever.
Scientists call it a robot. Nonetheless, it is also made from genetically unmodified cells from frogs.
Researchers found the xenobots were sphere-shaped and made up of about 3,000 cells that could replicate. However, it happened only rarely and only in certain circumstances.
Xenobots used “kinetic replication,” a procedure that occurs at a molecular level and has never been seen before, at the scale of organisms or whole cells or organisms.
With artificial intelligence, the scientists then tried out billions of body shapes possibilities to make xenobots more efficient with this type of replication.
Their supercomputer’s best shape possibility was a C-shape that looks like Pac-Man. Next, they discovered it could see microscopic stem cells in a petri dish, it would collect hundreds of them inside of its mouth, and a couple of days later, the cell bundles formed new xenobots.
The parent xenobot spins a massive ball of stem cells that mature into a new xenobot.
Furthermore, this shape influences the xenobots behaviour to magnify this fantastic process.
Xenobot Technology
The xenobots are exceptionally new and very early technology, like the 1940s computer. Therefore, they do not have a practical application.
Nonetheless, according to scientists, the combination of artificial intelligence and molecular biology may have the potential to be used in several tasks throughout the body and its environments.
This might include regenerative medicine, inspecting root systems, and collecting microplastics in the oceans.
The vision of self-replicating biotechnology may be concerning as the scientists assured that the breathing machines were contained in a laboratory and were extinguished quickly.
Moreover, they’re biodegradable with the regulation of ethics experts.
The study was published in the peer-reviewed science journal PNAS.